A greenhouse is a building with glass walls and a glass roof. Greenhouses are used to grow plants, such as tomatoes and tropical flowers. A greenhouse stays warm inside, even during the winter. In the daytime, sunlight shines into the greenhouse and warms the plants and air inside. The darker the surface, the more heat is generated. The greenhouse panels are good at transmitting light, but not heat.
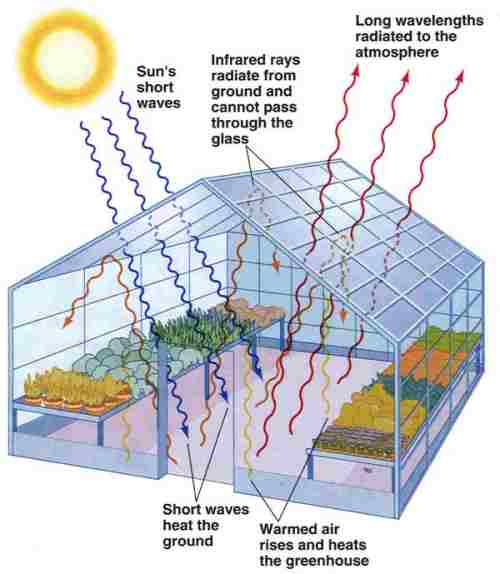
Greenhouses take the suns energy and heat and trap them in the greenhouse. This helps create massive amounts of heat relative to the outside and help plant grow and keep a constant temperature. This “greenhouse effect” make the greenhouse hotter and more humid than the air outside.
Although this method of trapping radiant heat in the winter to keep your plant toasty, in the summer it might get too hot. Many grower face their plants killed because of too much heat. Grower avoid this by:
- having proper and working ventilation, which can keep the flow of the greenhouse going; keeping hot air outside and cool air in
- keeping up air circulation, which can prevent dry air from lingering in the greenhouse
- use shade clothes to guard the greenhouse from those sun’s rays that get trapped in the greenhosue
Types of Greenhouse
Greenhouse structures of various types are used for crop production. Although there are advantages in each type for a particular application, in general there is no single type of greenhouse, which can be constituted as the best. Different types of greenhouses are designed to meet the specific needs. The different types of greenhouses based on shape, utility, material and construction are briefly given below:
Greenhouse Type Based On Shape:
For the purpose of classification, the uniqueness of cross section of the greenhouses can be considered as a factor. The commonly followed types of greenhouses based on shape are:
- Lean to type greenhouse.
- Even span type greenhouse.
- Uneven span type greenhouse.
- Ridge and furrow type.
- Saw tooth type.
- Quonset greenhouse.
- Interlocking ridges and furrow type Quonset greenhouse.
- Ground to ground greenhouse.
For more details, please visit: http://ecoursesonline.iasri.res.in/mod/page/view.php?id=1604
What is Greenhouse Technology?
Today about 92% of plants, raised by man, are grown in the open field. Since the beginning of agriculture, farmers have had to cope with the growing conditions given to them by Mother Nature. In some of the temperate regions where the climatic conditions are extremely adverse and no crops can be grown, man has developed technological methods of growing some high value crops by providing protection from the excessive cold and excessive heat. This is called Greenhouse Technology. “Greenhouse Technology is the science of providing favourable environment conditions to the plants”. It also protects the plants from the adverse climatic conditions such as wind, cold, precipitation, excessive radiation, extreme temperature, insects and diseases. An ideal micro climate can be created around the plants. Greenhouses are framed or inflated structures covered with transparent or translucent material large enough to grow crops under partial or full controlled environmental conditions to get optimum growth and productivity.

Reference:
